J Curve Currency Appreciation
Evidence from East Asia 401 price of imports will result in a decrease in the quantity demanded of imports. If the value of balance of trade is positive that is if the balance of trade lies above the zero line and the curve rises the balance of trade improves.

Acc 403 Week 9 Quiz 7 Chapter 14 15 Chapter Business Risk Quiz
J-curve definition implies an economic theory stating that under specific assumptions the trade deficit of a country is going to become worse initially after currencys DepreciationThis is primarily because of higher prices on the overall imports that tend to be higher in comparison to the lower volumes of imports.

J curve currency appreciation. Specifically the J-curve pattern is induced by both ASEANs currencies depreciation and appreciation against USD as indicated by the coexistence of insignificant or negative short-run. On the other hand devaluation or depreciation makes the imports from abroad expensive in terms of domestic currency rupees in case of India and therefore the imports tend to fall. The reverse J curve is a phenomenon where an appreciation of the currency can lead to an initial improvement before a longer term worsening of the trade bala.
The existence of a J-curve. Suppose a country devalues its currency. This J-curve effect is shown in Fig.
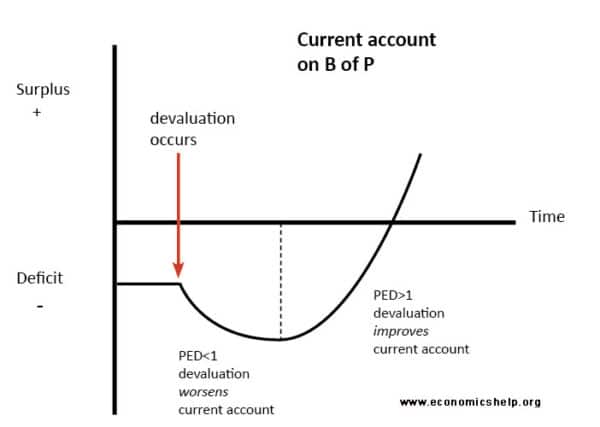
It first deteriorates the trade balance and then improves it later resembling a J-curve pattern. 358 where along the X-axis we measure time that is quarters after devaluation and on the Y-axis we measure the balance of trade. According to the J-curve effect after initial deterioration in response to the domestic currency depreciation trade balance will improve gradually due to a decline of export price in terms of the destination currency.
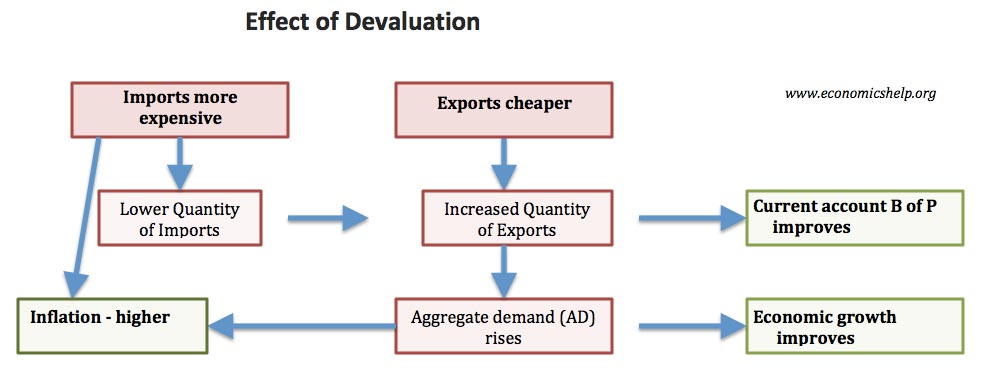
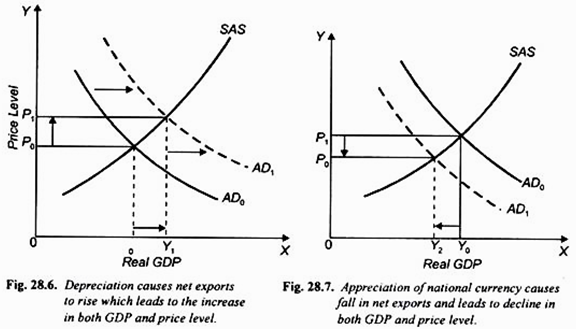
Lowering of the value of a currency of a country tends to raise its exports by making its goods cheaper for foreigners. A devalued currency means imports are more expensive and on the assumption that the volumes of imports and exports change little at first this causes a fall in the current account a bigger deficit or smaller surplus. Initially a countrys external trade deficit X-M might increase following a currency depreciation.
J-curve in international trade J-curve shows you the effect of currency devaluation or depreciation on the trade balance in a country. The theory of the J-curve is an explanation for the J-like temporal pattern of change in a countrys trade balance in response to a sudden or substantial depreciation. In economics the J curve is the time path of a countrys trade balance following a devaluation or depreciation of its currency under a certain set of assumptions.
The J-Curve is related to the Marshall-Lerner condition which states. If certain restrictions on demand and supply of imports and exports are met3 a depreciation of a currency will lead to an increase in the value of exports and a. However in the long-term demand becomes more price elastic and therefore the current account begins to improve.
GDP usually decreases before it increases after a currency depreciation B. Shock currency depreciation and the j-curve In the first half of 1994 Turkey experienced a shock currency depreciation followed by a steady appreciation as shown in Figure 1. Depreciation or devaluation is the decrease in value of that.
Quantities of imports will fall and quantities of exports will rise so real Net Exports will gradually improve. The effect of currency depreciation on the trade deficit. The J-curve effect refers to the observation that.
The J-curve effect implies that following a currency appreciation a countrys trade balance. The J-curve phenomenon which was introduced by Magee 1973 describes that in the short-run the effect on the trade balance of a devaluation or currency depreciation is due to time lags in the adjustment process. In economics the J-curve shows how a currency depreciation causes a severe worsening of a trade imbalance followed by a substantial improvement.
The J Curve effect a depreciation in the exchange rate can cause a deterioration of the current account in the short-term because demand is inelastic. The trade balance usually gets worse before it improves after a. The J-curve deals with the length and depth of a deterioration in the trade balance after a depreciation before its recovery to see if it will improve over its initial value in the long-run.
In addition to the concepts of exchange rates and trade balance to learn it you also need to understand the concept of elasticity of demand especially about the effect of time on the elasticity of demand. Economists often describe this phenomenon through the J curve. False According to the J-Curve a depreciation of the US dollar relative to the yen causes the quantities of imports to and exports from Japan to adjust gradually over the midterm 5-7 months.
A rapid and large depreciation of the yen was expected to have a positive impact on Japanese trade balance. Devaluation and the Balance of Trade. Also the impact of exchange rate depreciation may not be straightforward.
J-Curve Updated on September 28 2021 576 views What is J-Curve. In economics the J curve is the time path of a countrys trade balance following a devaluation or depreciation of its currency under a certain set of assumptions. Initially due to the price effect the increased value of imports would dominate the increased volume of.
The J-curve theory represents a short-term exception to the standard assumption applied in the GS model in which a currency depreciation causes a decrease in the trade deficit. Appreciation is the increase in the value of a currency compared to others and that currency can now buy more foreign money. The J Curve effect shows the possible time lags between a falling currency and an improved trade balance.
Improves before is worsens. The J-curve effect is a phenomenon that has been proven important for examining the impact in the trade balance after a depreciation. It is because other factors affect exports and imports including the elasticity of demand for traded goods and services product competitiveness global economic growth and domestic economic growth.
The J-curve effect implies that following a currency appreciation a countrys trade balance.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Devaluation Economics Help

Exchangerate Adjustments And The Balance Of Payments Power

Acc 206 Quiz 7 The Marshall Exchange Rate Conditioner

Qrops Ireland Private Company Singleton Moving To Ireland
Effects Of Depreciation And Devaluation Of The Exchange Rate

J Curve Effect Of Currency Depreciation Download Scientific Diagram
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Currency_Appreciation_Definition_Apr_2020-01-063bf4cdbc9e4f4d82fa4aa46738498d.jpg)
Currency Appreciation Definition

Exchangerate Adjustments And The Balance Of Payments Power


Posting Komentar untuk "J Curve Currency Appreciation"